You'll learn how to configure SSH access to your Virtual Machine and set up password-less login.
Log in to the virtual machine and install ssh server software:
$ sudo apt-get install openssh-server
Get your ip address with
$ ip address
You can now connect from another machine or your host computer:
$ ssh debian@<remote_host>
Replace
Windows has a built-in SSH client that you can use in Windows Terminal.
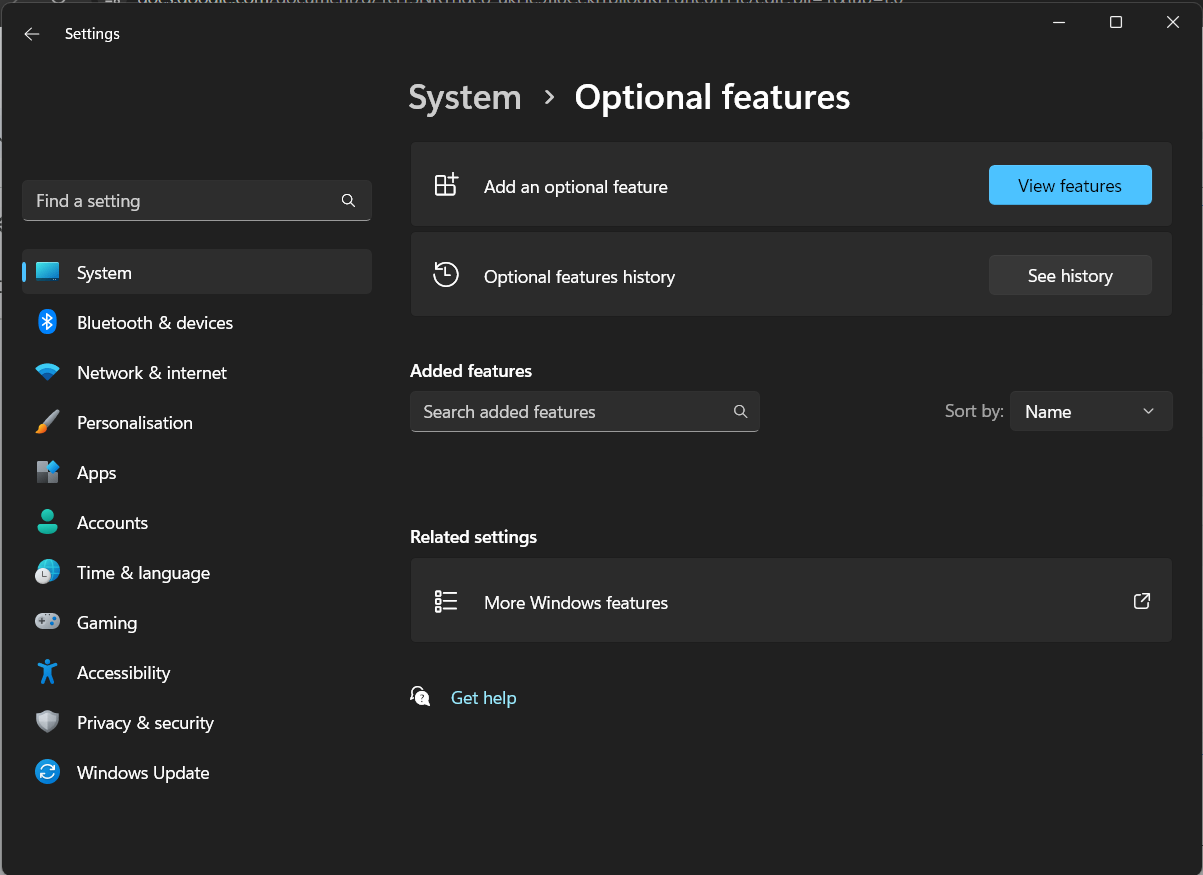
You can check that it is installed in Windows Settings > System > Optional features, then search for "OpenSSH" in your installed features.
On GNU/Linux Debian you can install the client with
$ sudo apt-get install openssh-client
We are going to generate a SSH key pair, which will allow us to connect without a password.
Create key
On your host (windows) generate your key pair.
PS> ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096
You will be asked for a location, accept default by hitting enter.
Then you will be asked if you want to protect the key with a password. This is a good practice, but for the exercises it can be painful because you will have to enter it often. Decision is up to you.
Upload key to vm
On windows you can use this trick
PS> type $env:USERPROFILE\.ssh\id_rsa.pub | ssh debian@<remote_host> "cat >> .ssh/authorized_keys"
On GNU/Linux
$ ssh-copy-id debian@<remote_host>
Connect without password
PS> ssh debian@<remote_host>
We want to connect to the Database Server from a Tool on our host machine. However, by default you cannot connect directly to a PostgreSQL server from an external connection. They are disabled by in pg_hba.conf (more on this in another lab).
Connect via SSH port forwarding
Before connecting you can specify a local port which will be mapped to a remote host and ip. Lets redirect traffic from the host DB port to the localhost DB port inside the virtual machine.
PS> ssh -L 5432:127.0.0.1:5432 debian@<remote_host>
Test the connection
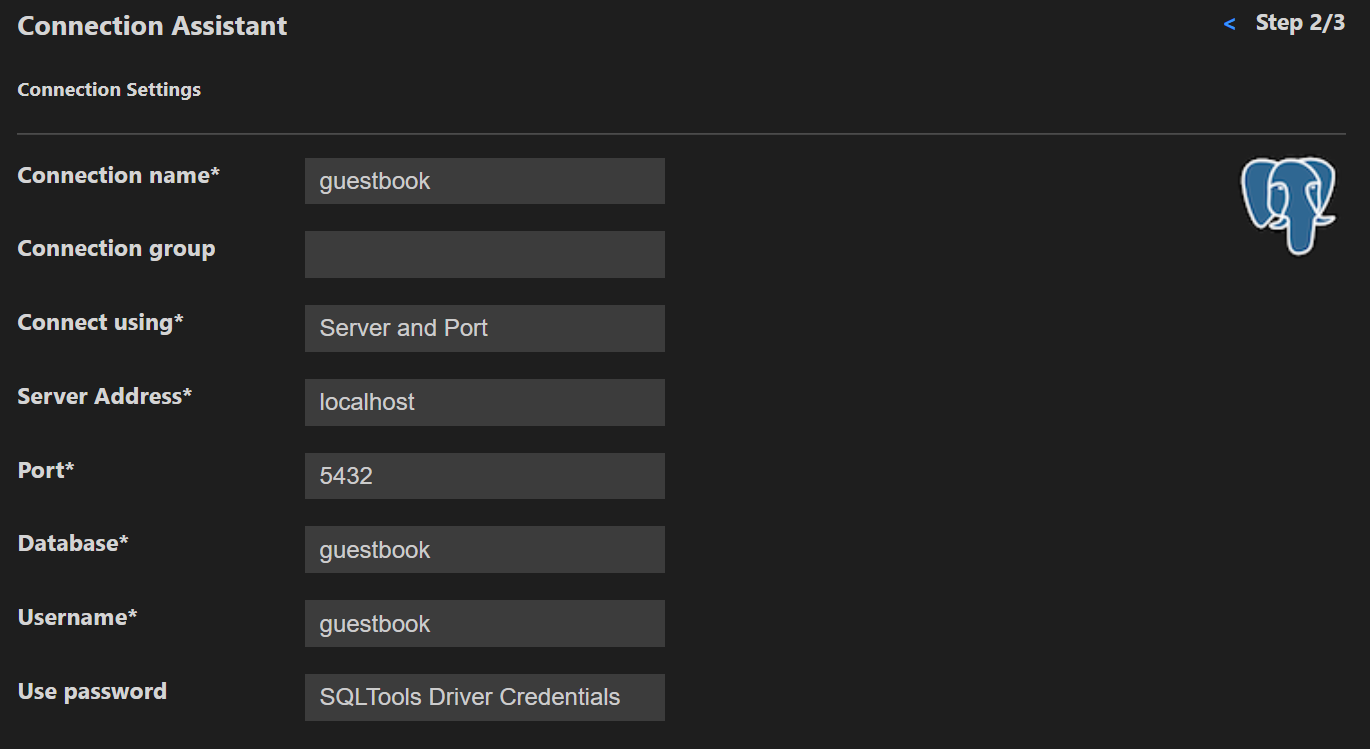
Use VScode SQLTools with PostgreSQL drivers to connect to the database:
Adapt the credentials according to your setting
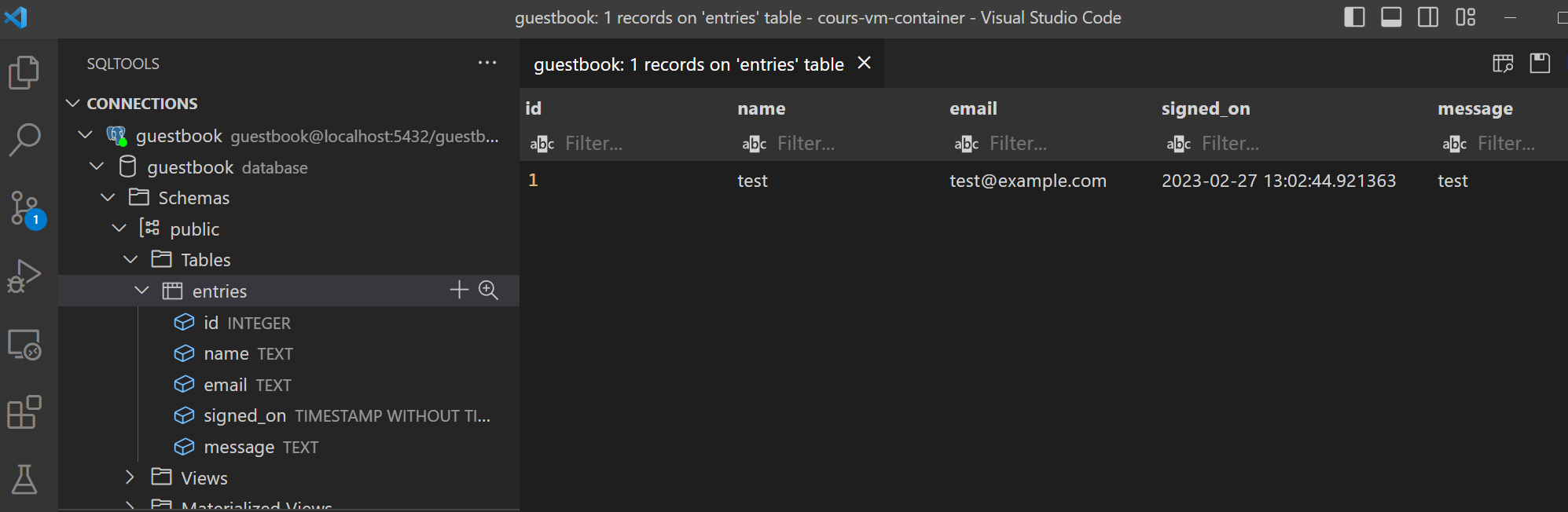
You can then explore the database.
You can use your new SSH key to authenticate with GitHub and remove the need to enter your password for every git clone, pull or push action.
Add key to your Account
Test your key
Git clone a repository with the git/ssh url: git@github.com:heg-web/[algopy-...].git

We are going to create a new virtual machine on a cloud provider. In modern cloud infrastructure, login is mostly done via SSH keys. The key is directly added to the virtual machine at creation and allows login without ever setting a password.
Add key to Switch Engines
Login with your edu-id account on https://engines.switch.ch/horizon/quickstart/#/
Switch Region to LS (on the top)
Go to Project > Compute > Key Pairs and click Import Public Key
Create your first virtual machine on switch engine
Use Quickstart > Instances > Create Instance

Create a simple virtual machine with the following options:
OS: Debian 12
CPU: 2
Ram: 2GB
Volume: 10GB / Standard
SSH Keypairs: your imported key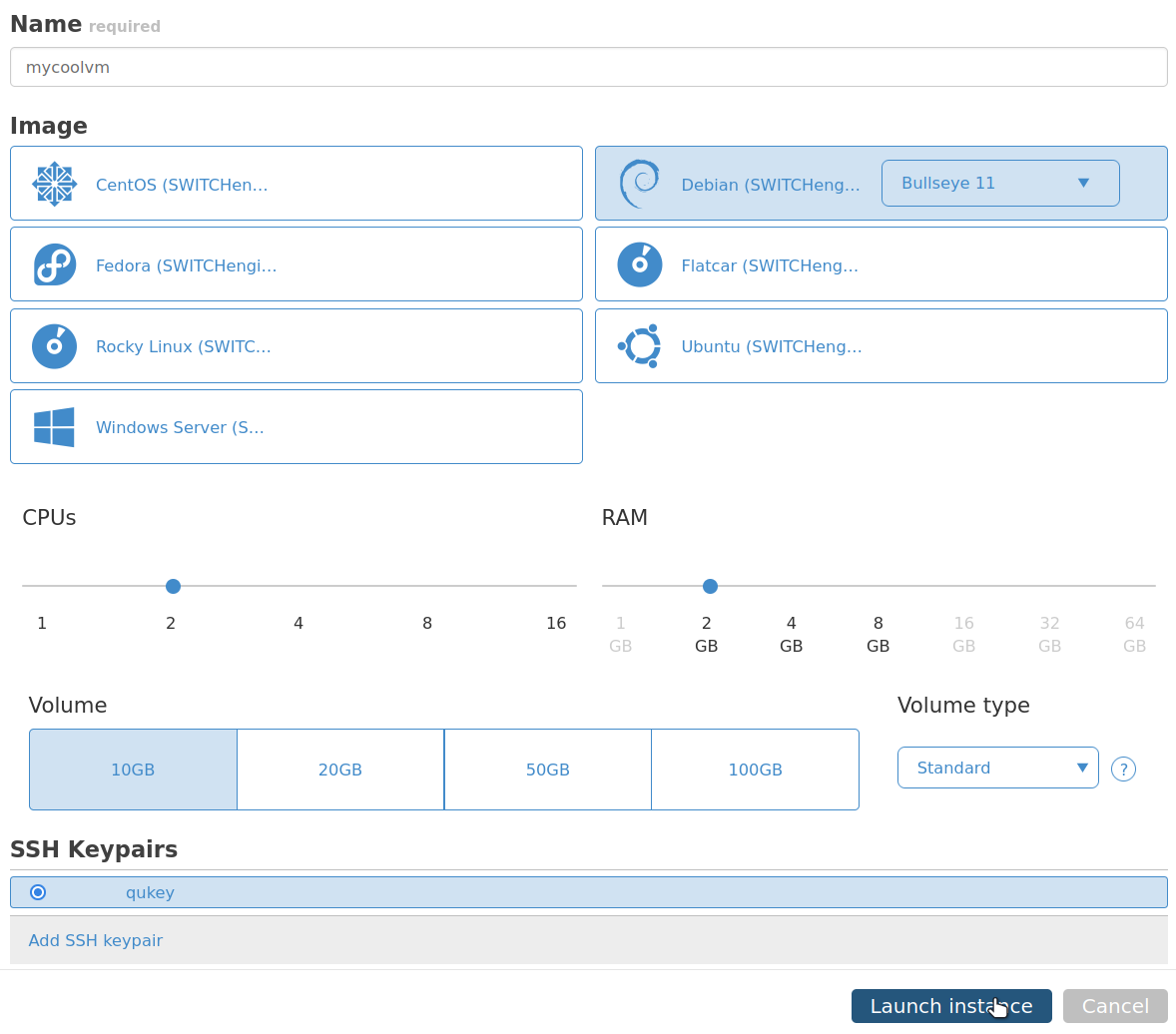
Connect to your new virtual machine
Use the displayed external ip to connect to your new machine from your host.
PS> ssh debian@<remote_host>
Run the lscpu command
$ lscpu
What is the Hypervisor used on this platform ?
Go into the switch engine instances and look at your virtual machines' advanced settings.
Which security Groups are applied?
Task Progress Check
Take a screenshot showing the ssh window with the result as well as the browser window showing your SWITCHengines vm instance and upload it below.
We are going to test creating a virtual machine on AWS
- Login to the AWS and go to EC2
- Go to Key pairs and actions > import key pair
- Upload your public key
- Go to instances and Launch an instance.
- Use Debian and
t3.micro - Select your newly uploaded key pair
- Launch and wait
- From the dashboard get the Public IPv4 of your instance
You can now connect to your vm from your computers'terminal with
PS> ssh admin@<remote_public_ip>
Run the lscpu command
$ lscpu
What is the Hypervisor used on this platform ?
As we have a virtual machine located in the US region we will try SSH Socks forwarding.
Reconnect via ssh but with Dynamic Port Forwarding
PS> ssh -D 7777 admin@<remote_host>
Use this socks proxy 127.0.0.1:7777 with one of your browsers.
For example in Firefox:
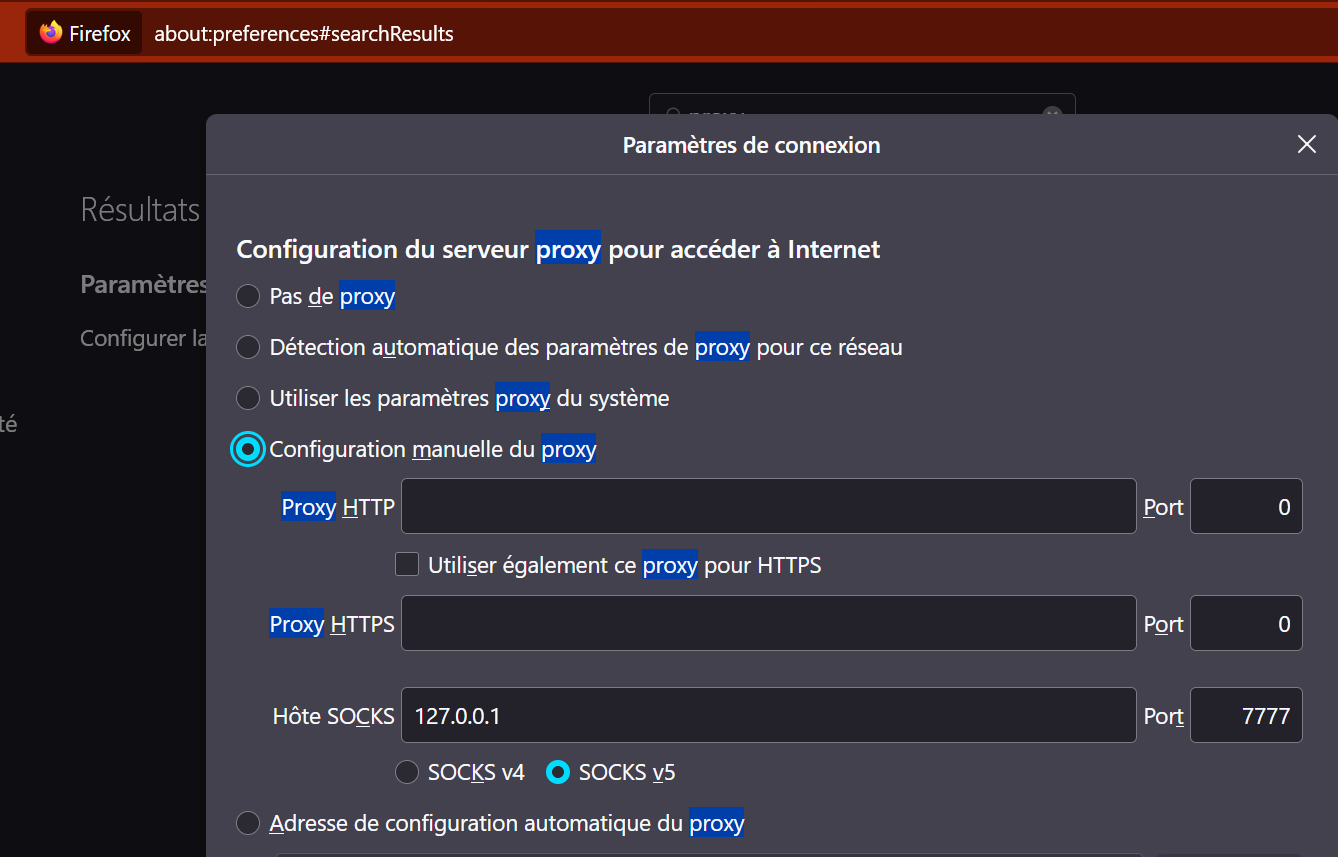
Where are we?
Now go to https://whatismyipaddress.com/
Try to play a video from https://www.rts.ch/
Does it work?
We are going to test creating a virtual machine on Google Cloud.
- Login to the Google Cloud Console
- If it's your first time create a project and enable compute api. You can follow this tutorial: Create a Linux VM instance in Compute Engine
- You should create a e2-micro instance in us-east region of your choice
- Edit the virtual machine options to add your PUBLIC SSH Key. After saving check the username linked to your key in the same place.
- Get the public ip address
You can now connect with
PS> ssh <username>@<remote_host>
Run the lscpu command
$ lscpu
What is the Hypervisor used on this platform ?