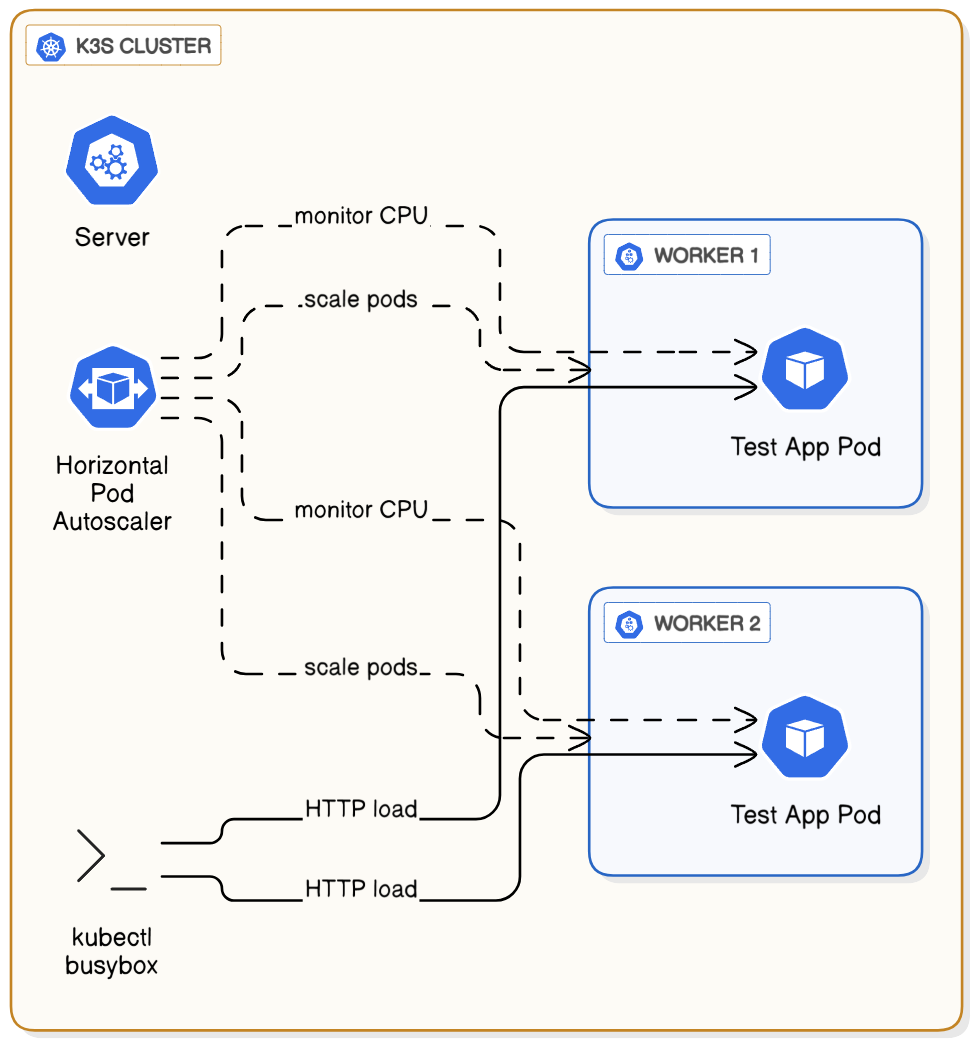
A HorizontalPodAutoscaler (HPA) automatically updates a workload resource (like a Deployment) to match demand.
- Horizontal scaling (scaling out) means adding more Pods to handle increased load.
- Vertical scaling (scaling up) would mean giving more CPU or memory to existing Pods.
The HPA is a core component of Kubernetes that allows applications to respond to traffic spikes without manual intervention and to save resources during quiet periods by scaling back down. In this walkthrough, we will deploy a test application and then apply a load to watch the HPA automatically increase and decrease the number of running pods.
Prerequisites
This lab requires a running K3s cluster managed by Rancher, as configured in a previous lab
Based on https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/run-application/horizontal-pod-autoscale-walkthrough/
For CPU-based autoscaling to work, our pods must declare how much CPU they request. This allows the HPA to calculate utilization as a percentage of the requested amount. We will deploy a sample php-apache application and configure its resources using the Rancher UI.
Create a Namespace
- Log in to Rancher and navigate to your
localcluster. - In the left menu, go to Cluster -> Projects/Namespaces.
- Click Create Namespace under default project
- Name:
hpa-demo - Click Create.
Create the Deployment
- In the left menu, navigate to Workload -> Deployments and click Create.
- Name:
php-apache - Namespace: Select
hpa-demofrom the dropdown. - Containers -> Container Name:
php-apacheContainer Image:registry.k8s.io/hpa-example - Networking: Set Service Type to:
Cluster IPand Port to80
Set Resource Requests and Limits
- In the same "Create Deployment" screen, scroll down to the container settings.
- Click Resources.
- Set CPU Reservation (Requests):
200(m stands for millicores; 200m is 0.2 of a CPU core). - Set CPU Limits:
500This tells Kubernetes to guarantee 200m CPU for this pod and to not let it use more than 500m. The HPA will use the 200m request as its baseline.
Click Create
You now have a deployment with one pod and an internal service to access it.
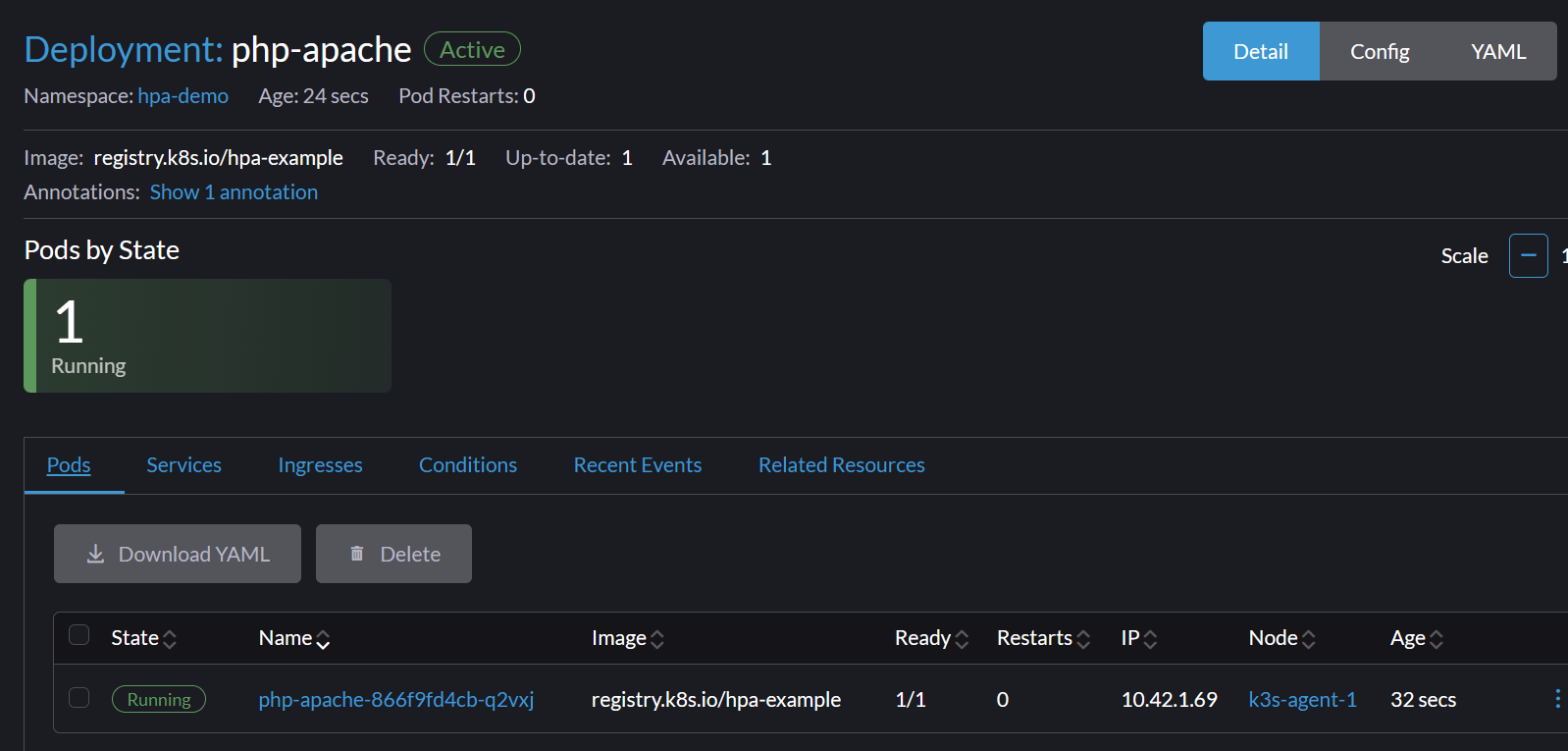
Now, let's create the HPA resource that will watch our php-apache deployment.
Navigate to HPAs
- In the left menu, go to Service Discovery -> HorizontalPodAutoscalers
Create the HPA
- Click Create.
- Name:
php-apache - Namespace:
hpa-demo - Target a resource: Select
Target Referenceand thenphp-apachefrom the dropdowns. - Minimum Replicas:
1 - Maximum Replicas:
10
Configure the Metric
- Under Metrics, (ignore warning).
- Metric Type:
Resource - Resource Name:
CPU - Target Type:
Average Utilization - Average Utilization:
50
This configures the HPA to scale up when the average CPU usage across all pods exceeds 50% of their requested 200m (i.e., 100m).
Configure the behavior
- Under Behavior, Enable Configure scale down behavior
- Add Policy
- Type:
Pods - Value:
1 - Period seconds:
10 - Stabilization window seconds:
30
This will make the HPA more reactive, so we wait less during testing
Click Create.
Check the HPA Status
- You will see your new HPA in the list.
To trigger the autoscaler, we need to send traffic to our php-apache service. We'll run a simple busybox pod in a continuous loop to generate this load.
Open the Kubectl Shell
- In the top-right of the Rancher UI, click the Kubectl Shell icon.
Run the Load Generator
- Execute the following command in the shell. This command creates a temporary pod that hits the php-apache service in a loop.
$ kubectl run -n hpa-demo -i --tty load-generator --rm --image=busybox:1.28 --restart=Never -- /bin/sh -c "while sleep 0.01; do wget -q -O- http://php-apache; done"
It will be automatically removed (--rm) when you stop the command.
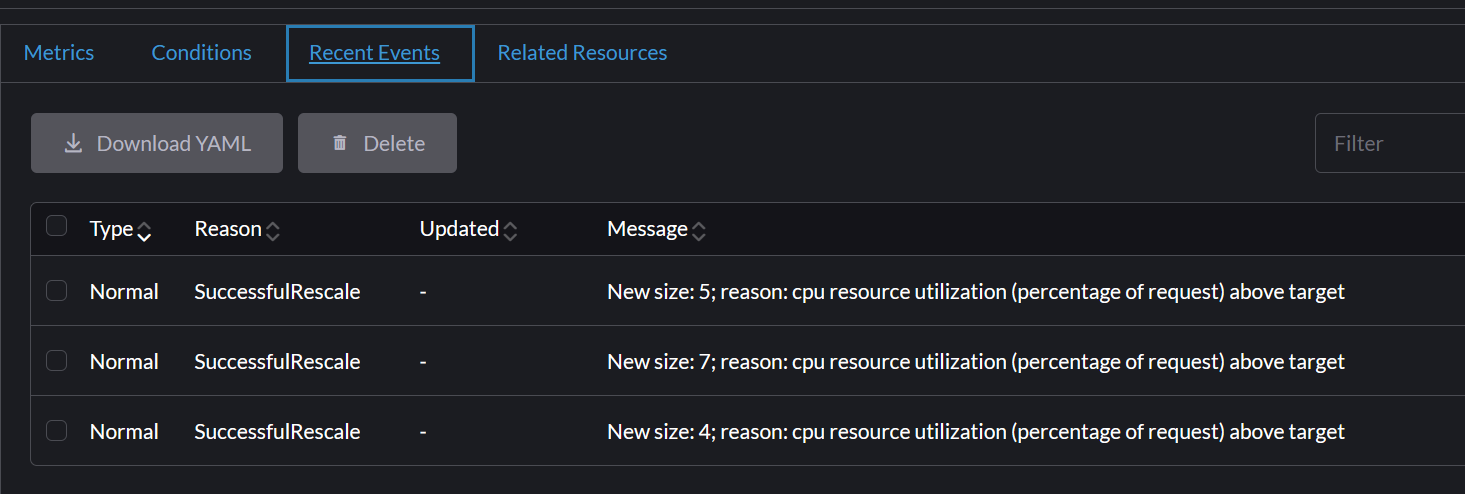
Watch the Deployment Scale
- Navigate back to the Service Discovery -> HPAs page.
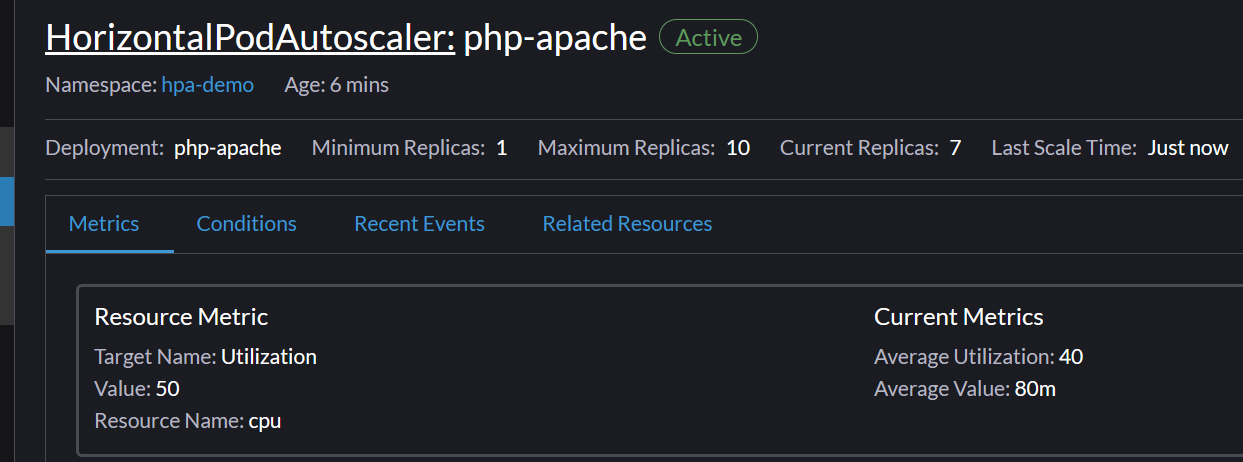
- Observing the CPU usage in the Current Metrics >Average Utilization it will go up to
350. - Navigate to Workload -> Deployments.
- Find the
php-apachedeployment. You will see the number of pods start to increase. - The HPA will add pods until the average CPU utilization comes back down to the
50target. It may stabilize at around7pods. - You can click on the deployment name to see the new pods being created.
Task Progress Check
Take a screenshot that shows two things side-by-side:
- The HPA detail page showing the high CPU usage and the replica count scaled up (e.g., 7 of 10).
- The
php-apachePods page showing the corresponding number of running pods.
Upload the screenshot to complete the lab.
Now we'll stop the load and watch the HPA scale the application back down to its minimum size.
Stop the Load Generator
- Go back to the browser tab where your Kubectl Shell is running.
- Press
Ctrl + Cto stop wget Followed byCtrl + Dto exit the container. the command. Theload-generatorpod will be terminated automatically. - If you hit
Ctrl + Ctwice or the pods still exist in an error/terminated state manually delete it before trying to generate a load command again.
Observe the Scale-Down
- Navigate back to the Service Discovery -> HPAs page.
- The CPU usage in the Current Metrics >Average Utilization to
0. - Go to Workload -> Deployments. After a few minutes, you will see the number of pods for the
php-apachedeployment decrease and stabilize back at the configured minimum of 1.
To remove all the resources created in this lab you can delete its namespace:
- Navigate to Cluster -> Projects/Namespaces.
- Find the
hpa-demonamespace, click the three-dot menu on the right, and select Delete. - Confirm the deletion. This will remove the namespace and everything inside it (Deployment, Service, HPA).